Quantum_Computing
[toc]
- Books
- Courses and resources
- Advice
- News
- 二、谷歌的量子霸权之路
- Quantum Programming
- 量子運算程式語言「Q#」誕生
- Quantum Computer
- New quantum computer design to predict molecule properties
- Topological quantum computer
- Quantum computer solves problem, without running
- Google combines two main quantum computing ideas in one computer
- Russian physicists discover a new approach for building quantum computers
- Efficient distributed quantum computing
- Magic states offer surprisingly low error rates for quantum computing
- What's the noise eating quantum bits?
- Simple is beautiful in quantum computing
- A new kind of quantum computer
- Quantum Simulator
- Quantum Memory
- Quantum Algorithm
- Quantum information
- Transferring quantum information using sound
- Deterministic teleportation of a quantum gate between two logical qubits
- Software engineer announces experiment with post-quantum cryptography in Chrome
- Scientists produce status check on quantum teleportation
- New principle sets maximum limit on quantum information communication
- Quantum machine learning
- Papers
- Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
- How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
- Neural networks take on quantum entanglement
- Physicists extend quantum machine learning to infinite dimensions
- How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
- Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
- How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
- Quantum algorithm could help AI think faster
- Articles
- 量子计算
- 量子(Quantum)
- 量子位(Qubit)
- 叠加(Superposition)
- 纠缠(Entanglement)
- Quantum SVM
- 1. 量子线路
- 2. 支持向量机
- 2. 1. 线性分类器的模型
- 2. 2. 转化为对偶问题
- 2. 3. 非线性分类的核函数
- 3. 量子支持向量机
- Quantum Gate
Books
Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Hardcover)
介紹量子邏輯閘, 量子代數符號與算法
Quantum Machine Learning: What Quantum Computing Means to Data Mining (Hardcover)
先介紹古典的機器學習算法, 再介紹對應的量子算法以及物理上的圖像
Quantum Information Theory, 2/e (Hardcover)
介紹量子夏農理論, 有雜訊的量子資訊理論, 量子協議, 量子通訊
Courses and resources
The Quantum Internet and Quantum Computers: How Will They Change the World?
Reviews for Quantum Information and Computing from NPTEL | Class Central
GitHub - krishnakumarsekar/awesome-quantum-machine-learning
Advice
If I'm interested in quantum computing, should I major in computer science or physics? How realistic is it to work in quantum computing?
-
If you come via a CS route you will definitely end up doing theoretical work because there aren't actually any full scale quantum computers for you to play with yet. If you do physics you can end up doing theory or experiment.
Physicists also do theoretical work, but typically of a different sort to computer scientists. They try to figure out new ways of building quantum computers, apply ideas from quantum information to other fields of physics, and work on the foundations of quantum theory. Computer scientists are more likely to be found working on quantum algorithms and complexity, although several groups now do semantics, programming languages, logics and things like that as well.
News
-
NEC開發的「量子退火(Quantum annealing)」方式擅長從龐大的選項中導出最合適答案。該公司將在2018年內製作基礎線路,2023年之前投入數十億日元開發實體機。
NEC的技術在顯示計算能力的「量子比特」方面達到2000~3000量子比特,能夠迅速選出數百個城市各時間點最合適的交通路線。在量子退火方式方面領先的加拿大D-Wave系統公司的技術為2000量子比特左右。NEC表示,「即使是同樣的量子比特數,我們的性能也將更高」。力爭推進産官學合作,10年內將計算能力提高至1萬量子比特。
CES 2018: Intel's 49-Qubit Chip Shoots for Quantum Supremacy
CES 2018: Intel's 49-Qubit Chip Shoots for Quantum Supremacy - IEEE Spectrum
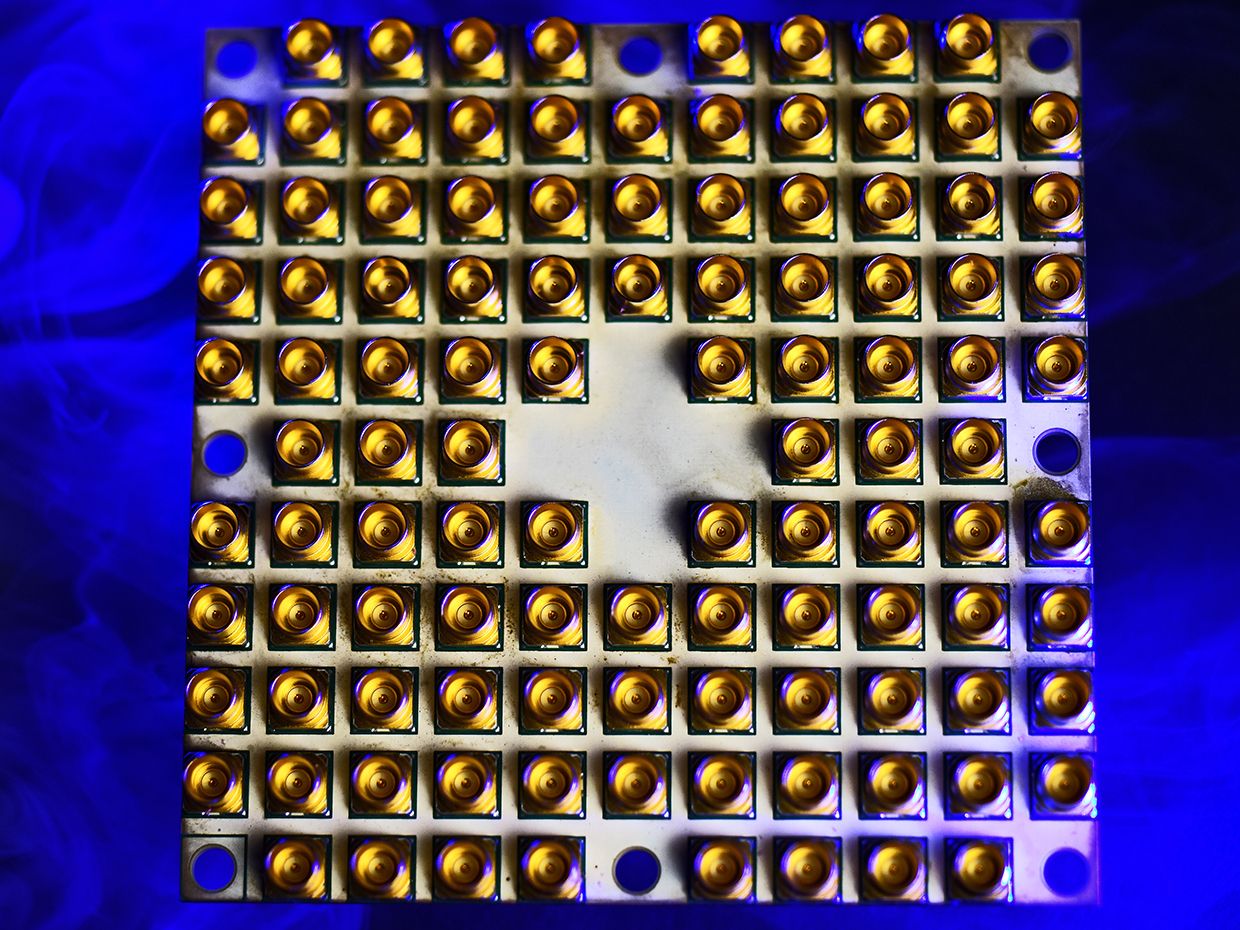
49 qubits: enough qubits to possibly enable quantum computing that begins to exceed the practical limits of modern classical computers.
It’s a milestone that Google and IBM researchers have also been targeting because it could usher in the moment of so-called “quantum supremacy,” when quantum computing can outperform classical computing.
“Around 50 qubits is an interesting place from a scientific point of view, because you’ve reached the point where you can’t completely predict or simulate the quantum behavior of the chip,” he says.
Intel’s roadmap suggests researchers could achieve 1,000-qubit systems within 5 to 7 years.
One important step involves implementing “surface code” error correction that can detect and correct for disruptions in the fragile quantum states of individual qubits. Another step involves figuring out how to map software algorithms to the quantum computing hardware. A third crucial issue involves engineering the local electronics layout necessary to control the individual qubits and read out the quantum computing results.
17-qubit arrays that have the minimum number of qubits necessary to perform surface code error correction.
The superconducting qubit architecture involves loops of superconducting metal that require extremely cold temperatures of about 20 millikelvin (-273 degrees C).
The company has also evenly split its quantum computing investment between the superconducting qubit architecture and another architecture based on spin qubits in silicon.
Such spin qubits are generally smaller than superconducting qubits and could potentially be manufactured in ways similar to how Intel and other chip-makers manufacture conventional computer transistors.
-
在3月5日的美国物理学会的一次会议上,科学家们报告,谷歌正在测试一台72位量子位的量子计算机,与该公司之前的9位比特芯片相比,将是一次巨大的飞跃。
来自谷歌的物理学家Julian Kelly表示,该小组希望使用具有更多量子位的芯片来首次实现量子霸权,即达到所有传统计算机无法实现的计算能力。
与采用0或1为比特的传统计算机不同,归功于量子叠加效应,一个量子位可以是0,1或两者的混合体。实现量子霸权则需要一台超过50量子位的计算机,目前科学家们仍在努力实现控制这么多精细的量子体。

图 | 谷歌的72位量子芯片的计算能力可能会首次实现超越传统计算机
由于芯片中的量子比特排列成类似松果鳞片的图案,因而谷歌的72位量子比特的计算机也得到了一个形象的绰号:“狐尾松”(Bristlecone),目前该计算机还在测试中。
来自加州大学圣巴巴拉分校的谷歌物理学家John Martinis表示,他们刚开始进行该计算机的测试,并且目前的测试情况非常乐观。另外,他补充到,如果一切顺利的话,量子霸权的演示可能在几个月内实现。
谷歌是目前致力于将量子计算机成为现实的几家公司之一。在2017年11月,IBM也宣布测试一台50位量子计算机,随后英特尔在今年1月宣布测试具有49位量子比特的芯片。
-
美国时间3月5日,谷歌研究博客(Google Research Blog)丢出一个深水炸弹——Bristlecone,这是一个72量子比特的量子芯片。
谷歌Google此次公布的Bristlecone的量子芯片使用了一种新的架构,允许单个阵列上的72个量子比特具有重叠设计,将两个不同的网格放在一起。
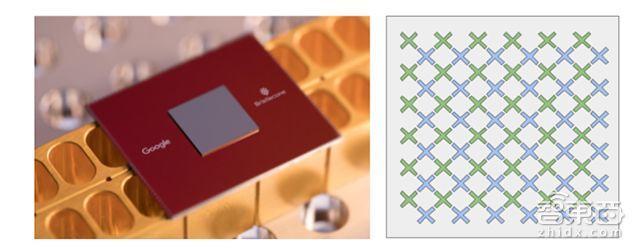
▲左边是谷歌最新的72量子比特量子处理器Bristlecone|右边是图示:每个“X”代表一个量子比特,量子比特之间以线性阵列方式相连
Google利用称为量子纠错(Quantum Error Correction)的专门流程对Bristlecone进行了优化,以尽可能降低错误率。正是谷歌这样的设计,让Bristlecone量子芯片在达到72量子比特的同时也实现了1%的错误率。
一时间,科技圈炸开了锅,因为这意味着,在实现量子计算这条赛道上,目前谷歌可能成为了领跑的那一个(关于量子计算机更通俗易懂的报道可以参看:量子计算机有多可怕一秒破译全世界所有密码!)。
二、谷歌的量子霸权之路
谷歌宣布研制出低错误率、72量子比特的量子芯片Bristlecone,并且正在往实现72量子比特的量子计算机的方向上推进,虽然72量子比特非常令人兴奋,但是从量子芯片到量子计算机,谷歌要做的工作还有很多。
2017年12月,来自德国Jülich超级计算中心(Jülich Supercomputing Centre),中国武汉大学和荷兰格罗宁根大学(the University of Groningen)的研究人员宣布,他们打破了在经典超级计算机上可以模拟量子比特数量的世界纪录。
该团队能够在超级计算机上模拟46个量子位,打破了之前45个量子位的记录。尽管45和46量子比特之间的差别可能看起来很小,但是,每增加一个量子比特,其对于各方面的要求都是指数性增加的。通常情况下,如果其他条件相同,每个额外量子比特的内存需求会翻倍。
因此目前,最强大的超级计算机只能模拟46个量子比特,并且对于需要模拟的每个新量子比特而言,其存储需求通常会增加一倍。
因此,要模拟一个72量子比特的量子计算机,我们需要数百万倍的RAM(Random-Access Memory,随机存取存储),也就是2的(72-46)次方倍数。外媒Tom’ Hardware认为我们很可能无法在超级计算机中达到这样体量的RAM。
如果谷歌正在研究的72量子比特的量子计算机能够比我们最强大的超级计算机更快地运行任何算法,那么量子霸权时代将会到来。对此,谷歌也表示:“我们乐观但同时也是谨慎地认为,利用Bristlecone可以实现量子霸权”。
Quantum Programming
Microsoft Q
搶先Google、IBM一步,微軟推出秘密武器「Q#」,要讓量子電腦遍地開花|數位時代
量子運算程式語言「Q#」誕生
達成九月在Ignite開發者大會上的目標,微軟在本周宣布推出量子運算程式語言的Preview (預覽版)開發包,號稱可以降低商用量子計算技術的出錯率、增加穩定性,並加快量子運算走向商業化的速度。
這款開發包,有一個叫「Q#」的程式語言,可以協助開發者為量子電腦開發軟體,以及一台整合在微軟開發工具套件系列Visual Studio中的量子電腦模擬器「Q# library」,個人用戶最多可以模擬30個邏輯量子位能問題、企業客戶則可以模擬超過40個量子位能的計算問題,讓開發人員可以在一般電腦上利用Azure雲端服務測試量子電腦軟體,提供全套式的解決方案。
Programming exercises for Q# (Microsoft Quantum Katas)
微软开源 Quantum Katas,领先的量子编程解决方案 - 开源中国
Microsoft/QuantumKatas: Programming exercises for learning Q# and quantum computing
到目前为止,该项目主要涵盖以下主题:
基本量子计算门(Basic quantum computing gates):专注于量子计算中使用的主要单量子比特和多量子比特门的任务。
叠加(Superposition): 专注于在一个或多个量子比特上准备某个叠加状态的任务。
测量(Measurements):专注于使用测量来区分量子态的任务。
Deutsch--Jozsa 算法(Deutsch--Jozsa algorithm):专注于编写实现经典函数的量子的任务,以及 Bernstein-Vazirani 和 Deutsch-Jozsa 算法。
ScaffCC: Compilation, analysis and optimization framework for the Scaffold quantum programming language
NISQ演算法框架Cirq
量子技術即將進入青黃不接的階段,Google釋出NISQ演算法框架Cirq適應過渡期 | iThome
Google人工智慧量子團隊在第一屆量子軟體和量子機器學習國際研討會(QSML)上,發表了Cirq公開測試版,這是一個用於雜訊中等規模量子(Noisy Intermediate Scale Quantum,NISQ)電腦的開源框架,Cirq能讓研究人員在特定的量子處理器上開發量子演算法。該團隊也將Cirq用在Google的Bristlecone處理器上,而接下來他們還計畫在雲端提供該處理器。
NISQ是近期才由美國理論物理學家,同時也是加州理工學院理論物理學教授John Preskill提出的名詞,他在論文中提到,NISQ技術將在不久的未來實現,具有50到100量子位元的量子電腦,在理論上已經可以超過當前傳統數位電腦運算能力解決問題,但是在量子閘中的雜訊,將會限制能夠可靠執行的量子電路大小。
也就是說,程式在超過50量子位元的裝置上執行,很快的就難以在傳統的電腦上模擬,因此這些運算必須擺上量子電腦中計算,來完成傳統電腦無法完成的工作。目前這仍處在理論驗證階段,是一個高度抽象的工作,而且還無法應用在任何實際的用途。
不過,一旦人類到達了這個階段,我們就會處在NISQ的尷尬時期,因為我們的量子技術已經可以完成傳統電腦無法完成的事,卻無法提供演算法足夠的容錯能力,由於沒有足夠的量子位元來做錯誤糾正,所以無可避免的受雜訊干擾,以致於必須直接在物理層級使用不完美的量子位元。
因此現在電腦科學家要解決的問題,就是如何在這些不完美的NISQ處理器上開發量子演算法,並能善用受限的硬體優勢。這包括使用資料來解決問題中最困難的部分,而非糾結在演算法與硬體間的映射問題,另外,部分量子處理器存在複雜的幾何限制與其他細微差異,當開發者忽略這些細節,將會造成錯誤的量子計算。
Google人工智慧量子團隊為此在QSML上發表了Cirq公開Alpha測試版,這是一個專用於NISQ電腦的開源框架,能夠幫助研究人員了解NISQ電腦用於解決實務計算性問題的能力。Cirq在安裝後,就能讓研究人員在特定的量子處理器上撰寫量子演算法,該框架提供了精確的量子電路控制方法,像是使用原生量子閘指定量子閘行為、在裝置上放置適當的量子閘,或是在量子硬體的限制中,排成這些量子閘的時序。
Google提到,Cirq使用的資料結構經過最佳化,可以用於編寫或是編譯這些量子電路,以允許開發者充分利用NISQ架構。Cirq能夠支援在模擬器中執行這些演算法,同時也能整合未來量子硬體或更大的雲端模擬器。
Google同時宣布釋出OpenFermion-Cirq,OpenFermion是一個用來開發化學問題的量子演算法平臺,而OpenFermion-Cirq則是使用Cirq框架,來開發實現近期演算法的應用程式範例,編譯量子模擬演算法的開源函式庫,能將量子化學問題建構為低深度量子演算法,使研究人員可以把化學問題的細節,轉成高度最佳化的訂製量子電路,並在特定的硬體上運作,執行像是模擬分子或是複雜材料的特性等工作。
量子運算將會需要跨產業以及學界的合作,Google人工智慧量子團隊在建構Cirq時,就與包括劍橋與NASA在內的不同機構合作,以獲取演算法設計的回饋與意見。該團隊提到,他們正將Cirq應用在Google的Bristlecone處理器上,在不久的將來,也會在雲端服務提供該處理器,屆時Cirq將成為開發人員在該處理器上編寫程式的介面。現在Cirq以Apache 2授權在GitHub上公開,研究人員已經可以加入NISQ演算法開發。
ProjectQ – Open Source Software for Quantum Computing
QASM
Quantum Architectures: qasm2circ
QASM is a simple text-format language for describing acyclic quantum circuits composed from single qubit, multiply controlled single-qubit gates, multiple-qubit, and multiple-qubit controlled multiple-qubit gates.
qasm2circ is a package which converts a QASM file into a graphical depiction of the quantum circuit, using standard quantum gate symbols (and other user-defined symbols). This is done using latex (specifically, xypic), to produce high-quality output in epsf, pdf, or png formats.
量子程式語言的程序驗證
Quantum Computer
New quantum computer design to predict molecule properties
New quantum computer design to predict molecule properties
the standard equivalent for bits in quantum computing are qubits, which are bosons. Trying to simulate fermions (matter) using bosons (qubits) is inefficient
Quantum computation with majoranas previously relied on combining four or six majoranas into a single qubit. But you don't necessarily have to make majoranas into qubits
since you only need two majoranas to make a fermion instead of four or six for a qubit.
Topological quantum computer
Quantum computer solves problem, without running
Quantum computer solves problem, without running
"counterfactual computation," inferring information about an answer, even though the computer did not run.
quantum bits can be placed in superpositions of one and zero, as opposed to classical bits, which are either one or zero.
"It seems absolutely bizarre that counterfactual computation – using information that is counter to what must have actually happened – could find an answer without running the entire quantum computer,"
quantum interrogation is a technique that makes use of wave-particle duality (in this case, of photons) to search a region of space without actually entering that region of space.
Kwiat's team succeeded in counterfactually searching a four-element database using Grover's quantum search algorithm. "By placing our photon in a quantum superposition of running and not running the search algorithm, we obtained information about the answer even when the photon did not run the search algorithm,"
Google combines two main quantum computing ideas in one computer
Google combines two main quantum computing ideas in one computer
With the second approach the qubits do not interact, instead they are kept at a ground state where they are then caused to evolve into a system capable of solving a particular problem. The result is known as an adiabatic machine
the researchers have attempted to gain the positive attributes of both approaches by creating a machine where they started with a standard quantum computer and then used it to simulate an adiabatic machine.
Russian physicists discover a new approach for building quantum computers
> an easier method to create a universal quantum computer using multilevel quantum systems (qudits),
>
> we demonstrated that correlations similar to those used for quantum information technologies in composite quantum systems also occur in non-composite systems
>
> ---
>
> a method of using entanglement between internal degrees of freedom of a single eight-level system to implement the protocol of quantum teleportation
>
> ---
>
> Quantum objects that are used to create qubits – ions, electrons, Josephson junctions etc. can only maintain a certain quantum state for a very short time.
>
> ---
>
> Superconducting qubits used to "survive" only for a few nanoseconds, but now they can be kept for milliseconds before decoherence
>
> ---
>
> Qudits are quantum objects in which the number of possible states (levels) is greater than two (their number is denoted by the letter D). There are qutrits, which have three states; ququarts, which have four states, etc.
>
> ---
>
> "A qudit with four or five levels is able to function as a system of two "ordinary" qubits, and eight levels is enough to imitate a three-qubit system.
>
> ---
>
> we obtained the value of mutual information (the measure of correlation) between virtual qubits isolated in a state space of a single four-level system,"
>
> ---
>
> on one qudit with five levels, created using an artificial atom, it is possible to perform full quantum computations
>
> ---
>
> fake coin algorithm: imagine that you have a number of coins, some of which are fake – they have the same image on the obverse and reverse sides.
>
> ---
>
> the "classical method", you have to look at both sides. With the Deutsch algorithm, you "merge" the obverse and reverse sides of the coin and you can then see a fake coin by only looking at one side.
>
> ---
>
> To run a two-qubit Deutsch algorithm, for example, they proposed using a nuclear spin of 3/2 with four different states.
>
> ---
>
> superconducting circuits require five levels: the last level performs an ancillary role to allow for a complete set of all possible quantum operations.
>
> ---
>
> in certain physical implementations, it is easier to control multilevel qudits than a system of the corresponding number of qubits, and this means that we are one step closer to creating a full-fledged quantum computer.
>
Efficient distributed quantum computing
Efficient distributed quantum computing
if a quantum algorithm is to offer an exponential speed-up over classical computing, there must be a large entangled state at some point in the computation and it was widely believed that this translates into requiring a single large device.
A network of small quantum computers can implement any quantum algorithm with a small overhead.
The key breakthrough was learning how to efficiently move quantum data between the many sites without causing a collision or destroying the delicate superposition needed in the computation.
Magic states offer surprisingly low error rates for quantum computing
Magic states offer surprisingly low error rates for quantum computing
the leading approach to fault-tolerant quantum computing involves "magic states."
In order to create magic states, physicists take noisy quantum states and use a process called distillation to derive a smaller number of improved, i.e., higher fidelity, states.
up to 90% of a quantum computer's qubits are needed to create magic states, before any real computing can be done.
to minimize the noise in raw magic states (before any distillation) in order to reduce the number of distillation steps required,
raw magic states can have a fidelity that is superior to that of the operations that created them.
qubits are more sensitive to noise when the code distance (which is related to the number of qubits in a row of a lattice) is small
more stable when the code distance is larger.
For one type of magic state, for example, the new protocol can reduce the error due to noise by more than 20 times compared to previous protocols. As a result, the number of raw magic states required can then be reduced by a factor of 15.
What's the noise eating quantum bits?
What's the noise eating quantum bits?
Calculations have confirmed experimental evidence that oxygen molecules adsorbed on the surface of the SQUID are the most likely source of low-frequency magnetic noise.
the ability to develop SQUID-based quantum computers will require the stored magnetic data survive for long times.
In quantum computing, quantum information is lost due to a loss of synchronization (dephasing) in the electronic flow and energy relaxation. Magnetic flux noise is a dominant source of dephasing and energy relaxation in superconducting qubits.
the detrimental noise is from unpaired magnetic defects on surfaces of superconducting devices. Theoretical predictions singled out oxygen as the cause of noise in these systems.
Surface treatment with ammonia and improving the sample vacuum environment dramatically reduced the surface contamination (to less than one oxygen molecule per 10 nm2), minimizing magnetic noise.
Simple is beautiful in quantum computing
Simple is beautiful in quantum computing

Quantum computers use electron spin orientation at a defect site in diamond to store information. The electron spin can be up (+1), down (-1), or anything in between. The spin (left, red arrow) is represented as a vector on a sphere. To change the spin from Position 1 to 2 normally requires two separate optical pulses. However, here a particular single pulse has accomplished the same electronic transition. This single pulse makes the electron travel on a geometric loop, analogous to a Möbius strip (right, a surface with one side and one boundary), such that its position is changed in a robust way after completing the loop. Credit: US Department of Energy
The simple gates reorient electron spin on defect sites in diamond. This new finding would allow faster and more efficient manipulation of the electron spins or qubits.
Researchers exert a new form of fast geometric control on the electron's spin orientation.
As an added bonus, the new gates are also less sensitive to noise than today's operations (specifically, sequential, multi-pulse operations).
Similar to classical computers, quantum computers are designed to operate on quantum bits. An extraordinary property of qubits is that they can be of any value equal to or between -1 and +1, until we measure them.
Diamond is a very promising material for quantum information processing.
When the nitrogen is next to a missing carbon atom in the crystalline lattice, this is called a nitrogen-vacancy defect.
Its spin can be initialized, manipulated, and "read out" with a laser at room temperature,
This single impurity can emit one photon at a time. A photon can carry one qubit of information.
A geometric gate relies on the evolution or geometric path of the spin instead of energy differences involved in the gates used in traditional computers.
The geometry of the cycle is controlled by the single laser pulse and determines the final gate operations and electronic transitions. Further, careful control of the pulse energy significantly improved the fidelity of the electronic transition compared to traditional multi-pulse techniques
A new kind of quantum computer
A new kind of quantum computer
Light quanta (photons) can be used as information carriers and act as qubits, but to use them in a quantum computer they must interact with each other.
Read more at: https://phys.org/news/2017-11-kind-quantum.html#jCp
Under normal conditions, however, light does not interact with itself and so the challenge is to create correlations between them. The key idea of their new paper is to allow light photons from an atom to interact with their own mirror image reflections.
Read more at: https://phys.org/news/2017-11-kind-quantum.html#jCp
That delay, the scientists show, results in the combined waveform of the photons being so complex that in principle any quantum computation can be achieved by simply measuring the emitted photons.
Read more at: https://phys.org/news/2017-11-kind-quantum.html#jCp
Quantum Simulator
World's fastest quantum simulator operating at the atomic level
World's fastest quantum simulator operating at the atomic level
the post-K cannot even calculate the precise energy, the most basic property of matter, when the number of particles in the system is more than 30.
a "quantum simulator," has been proposed, in which quantum mechanical particles such as atoms are assembled into an artificial strongly correlated system whose properties are known and controllable.
they have succeeded in simulating the motion of electrons of this strongly correlated system that is modulated by changing the strength of interactions among many atoms in the ensemble.
Quantum Memory
How can you tell if a quantum memory is really quantum?
How can you tell if a quantum memory is really quantum?
Conventional protocols for testing for space-like correlations often use two characters, Alice as the sender and Bob as the receiver of quantum states. But since quantum memories involve time-like correlations, the protocol needs only a single character, whom the researchers call Abby, to act as both the sender and receiver at different times. In the test proposed in the new study, by comparing the relative frequencies of the signals that Abby sends and receives, it is possible to estimate the time-like entanglement and therefore certify that a quantum memory can store quantum information.
Quantum Algorithm
Parrondo's paradox with a three-sided coin
Link Between the P≠NP Problem and the Quantum Nature
The Astounding Link Between the P≠NP Problem and the Quantum Nature of Universe
How many NP problems can be made efficient with quantum computing?:QuantumComputing
cc.complexity theory - Problems Between P and NPC - Theoretical Computer Science Stack Exchange
Will Quantum computing power help us eventually to verify P=NP or vice versa?
Will Quantum computing power help us eventually to verify P=NP or vice versa? - Quora
Quantum algorithms that are solvable in polynomial time belong to the class BQP. That stands for Bounded error Quantum Polynomial time.
Researchers implement 3-qubit Grover search on a quantum computer
Researchers implement 3-qubit Grover search on a quantum computer
Previous research has shown that Grover's search algorithm, proposed in 1996, is an optimal quantum search algorithm, meaning no other quantum algorithm can search faster.
"Additionally, this is the first implementation of the algorithm using Boolean oracles, which can be directly compared with a classical search."
So, for example, for a single search iteration on a database of 8 items, a classical algorithm makes one random query and, if that fails, it makes a second random guess—in total, guessing 2 out of 8 items, resulting in a 25% success rate.
Grover's algorithm, on the other hand, first initializes the system in a quantum superposition of all 8 states, and then uses a quantum function called an oracle to mark the correct solution.
for a single search iteration on an 8-item database, the theoretical success rate increases to 78%.
The researchers also tested Grover's algorithm on databases that have two correct solutions, in which case the theoretical success rates are 47% and 100% for classical and quantum computers, respectively. The implementation demonstrated here achieved success rates of 68% and 75% for the two oracle types—again, better than the highest theoretical value for classical computers.
首次理論證明:Science論文提出超越經典計算的量子算法
Quantum information
Transferring quantum information using sound
Transferring quantum information using sound
These microscopic flaws in the crystal lattice can be used like tiny switches that can be toggled between a state of higher energy and a state of lower energy using microwaves.
Just like a tuning fork, this rod can then be made to vibrate—however, these vibrations are so small that they can only be described using quantum theory.
As the research team has now been able to show using simulation calculations, any number of these quanta can be linked together in the diamond rod via phonons. The individual silicon atoms are switched on and off using microwaves. During this process, they emit or absorb phonons. This creates a quantum entanglement of the silicon defects, thus allowing quantum information to be transferred.
Deterministic teleportation of a quantum gate between two logical qubits
耶魯實現量子門的隱形傳輸,模塊化量子計算的關鍵進展 - 幫趣
[1801.05283] Deterministic teleportation of a quantum gate between two logical qubits
這種架構中的模塊彼此之間具有自然隔離,通過更大系統減少不必要的相互作用。然而,根據研究人員的說法,這種隔離也使得在模塊之間執行運算成爲一個明顯的挑戰。量子門傳輸是實現模塊間運算的一種方式。
Chou 表示,「我們的工作首次展示了這種協議,其中經典通信實時發生,允許我們實現『確定性』運算,每次都能執行期望的運算。」
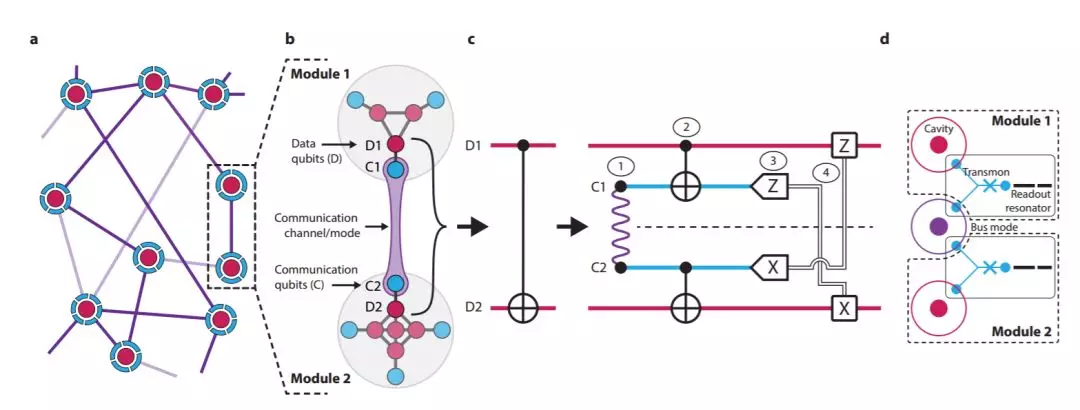 圖 1:模塊化架構和傳輸 CNOT 門的構造。
圖 1:模塊化架構和傳輸 CNOT 門的構造。實用量子計算機的計算速度將能超越當前超級計算機幾個數量級。耶魯大學的研究人員站在了開發首個實用量子計算機的前沿,用超導線路完成了量子計算的開創性工作。
量子計算是通過稱爲量子比特的相互作用來完成的,這種數據容易出錯。在實驗量子系統中,「邏輯」量子比特由「輔助」量子比特監控,以便立即檢測和糾正錯誤。Schoelkopf 表示,「我們的實驗第一次演示了邏輯量子比特之間的兩比特運算。這是使用可糾錯量子比特進行量子信息處理的里程碑。」
Software engineer announces experiment with post-quantum cryptography in Chrome
Software engineer announces experiment with post-quantum cryptography in Chrome
"the elliptic-curve algorithm will still provide the best security that today's technology can offer." On the other hand, if the post-quantum algorithm turns out to be secure then it will protect "the connection even against a future, quantum computer."
Scientists produce status check on quantum teleportation
Scientists produce status check on quantum teleportation
quantum teleportation – transferring the quantum structure of an object from one place to another without physical transmission
While theoretical proposals for a quantum Internet already exist, the problem for scientists is that there is still debate over which of various technologies provides the most efficient and reliable teleportation system.
teleportation-based optical communication needs an interface with suitable matter-based quantum memories where quantum information can be stored and further processed.
The development of good quantum memories would allow us to build quantum repeaters, therefore extending the range of teleportation.
New principle sets maximum limit on quantum information communication
New principle sets maximum limit on quantum information communication
According to this principle, the maximum amount of information is limited only by the quantum system's dimension, and does not depend on any physical resources previously shared by the communicating parties.
Pitalúa-García's principle of quantum information causality says that, after a quantum system of m qubits is transmitted from one party to another, the quantum information shared between the two parties cannot increase by more than 2m.
communicating parties share.
"The principle of information causality states that m classical bits can transmit m's worth of information,"
"On the other hand, quantum information causality states that m qubits can transmit 2m's worth of information. In this sense, a qubit can communicate twice the amount of information that a classical bit can communicate.
a qubit can be entangled with another qubit, while a classical bit cannot. It is entanglement that allows a qubit to communicate more information than a classical bit."
"The dimension of a quantum system can be understood as the number of different possible outcomes that are obtained when the system is subject to a measurement,"
"For example, a qubit has dimension two, because it gives one of two possible measurement results. Similarly, a system of m qubits has dimension 2^m. It is thus natural to expect that a system with bigger dimension can communicate more quantum information. This is proved mathematically by quantum information causality."
Quantum machine learning
Papers
Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
For the first time, physicists have performed machine learning on a photonic quantum computer, demonstrating that quantum computers may be able to exponentially speed up the rate at which certain machine learning tasks are performed—in some cases, reducing the time from hundreds of thousands of years to mere seconds. The new method takes advantage of quantum entanglement, in which two or more objects are so strongly related that paradoxical effects often arise since a measurement on one object instantaneously affects the other. Here, quantum entanglement provides a very fast way to classify vectors into one of two categories, a task that is at the core of machine learning.

In the new paper, the physicists addressed this challenge by representing vectors with quantum states, and then entangling the states before comparing the distance between them. As they explain, quantum computers are naturally good at manipulating vectors. So to do this, they used a small-scale quantum computer that manipulates optical qubits, or photons.
In the optical setup, one photon acts as an ancillary qubit, and is used to entangle another photon that encodes both the reference vector and the new vector. The resulting two-photon entangled state is used to classify two-dimensional vectors, whereas three- and four-photon entangled states can classify four- and eight-dimensional vectors, respectively. In general, different vector dimensions are needed to describe the properties of different real-world objects.
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
Neural networks take on quantum entanglement
Neural networks take on quantum entanglement
certain neural networks—abstract webs that pass information from node to node like neurons in the brain—can succinctly describe wide swathes of quantum systems .
In particular, the team studied neural networks that use two distinct groups of neurons. The first group, called the visible neurons, represents real quantum particles, like atoms in an optical lattice or ions in a chain. To account for interactions between particles, the researchers employed a second group of neurons—the hidden neurons—which link up with visible neurons.
Specifying a number for each connection and mathematically forgetting the hidden neurons can produce a compact representation of many interesting quantum states, including states with topological characteristics and some with surprising amounts of entanglement.
For instance, neural networks with only short-range interactions—those in which each hidden neuron is only connected to a small cluster of visible neurons—have a strict limit on their total entanglement.
the collection of states that they do represent efficiently, and the overlap of that collection with other representation methods, is an open problem that Deng says is ripe for further exploration.
Physicists extend quantum machine learning to infinite dimensions
Physicists extend quantum machine learning to infinite dimensions
Most quantum machine learning algorithms developed so far work only with problems involving discrete variables. Applying quantum machine learning to continuous-variable problems requires a very different approach.
To do this, the physicists had to develop a new set of tools that work with continuous variables. This involves replacing the logic gates that are used for discrete-variable states with physical gates, which work for continuous-variable states.
the physicists expect that the new algorithm for continuous variables could be experimentally implemented using currently available technology.
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
quantum effects could offer similar advantages for the emerging field of quantum machine learning (a subfield of artificial intelligence)
quantum effects can help improve reinforcement learning, which is one of the three main branches of machine learning.
quantum effects have the potential to provide quadratic improvements in learning efficiency, as well as exponential improvements in performance for short periods of time when compared to classical techniques for a wide class of learning problems.
Part of the reason for the difficulty in determining how quantum effects can improve machine learning is due to the unique set of challenges involved, beginning with the basic question of what it means to learn.
the scientists explain, since the machine and its environment may become entangled, blurring the boundary between the two.
the researchers expect that the systematic approach proposed here, which encompasses all three of the main branches of machine learning, will lead to the first steps in a complete theory of quantum-enhanced learning.
Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
Quantum computers could greatly accelerate machine learning
quantum computers may be able to exponentially speed up the rate at which certain machine learning tasks are performed—in some cases, reducing the time from hundreds of thousands of years to mere seconds.
quantum entanglement provides a very fast way to classify vectors into one of two categories, a task that is at the core of machine learning.
Classifying a small number of vectors in this way can be done very quickly. However, as the amount of data in the world rapidly increases, so does the time required for machines to process it.
the physicists addressed this challenge by representing vectors with quantum states, and then entangling the states before comparing the distance between them.
The resulting two-photon entangled state is used to classify two-dimensional vectors, whereas three- and four-photon entangled states can classify four- and eight-dimensional vectors,
"A GHz clock-rate quantum computer, if we can build it in the future, with the exponential speed-up, will take only about a second to estimate the distance between these two vectors after they are entangled with the ancillary qubit."
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence
How quantum effects could improve artificial intelligence

In the new study, the researchers' main result is that quantum effects can help improve reinforcement learning, which is one of the three main branches of machine learning. They showed that quantum effects have the potential to provide quadratic improvements in learning efficiency, as well as exponential improvements in performance for short periods of time when compared to classical techniques for a wide class of learning problems.
While other research groups have previously shown that quantum effects can offer improvements for the other two main branches of machine learning (supervised and unsupervised learning), reinforcement learning has not been as widely investigated from a quantum perspective.
Quantum algorithm could help AI think faster
Quantum algorithm could help AI think faster
As a rough guide, for a 10,000 square matrix, the classical algorithm would take on the order of a trillion computational steps, the first quantum algorithm some tens of thousands of steps and the new quantum algorithm just hundreds of steps. The algorithm relies on a technique known as quantum singular value estimation.
- [超越传统算法!全新量子算法可以帮助 AI 更快思考](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33725833)
> 第一个量子线性系统算法是在 2009 年由另外一组研究人员提出的,该算法是研究机器学习或人工智能的量子形式的鼻祖。
>
> **这套线性系统算法适用于大型数据矩阵。** 例如,交易者可以尝试预测未来的商品价格,该矩阵可以获取关于价格随时间变化的历史数据和关于可能影响这些价格的特征数据,比如货币汇率。该算法通过“反转”矩阵来计算每个特征之间的关联性,这些信息可以用来推断未来趋势。
>
> Zhao 解释道:“在分析矩阵时需要进行大量的计算,比方说当输入超过 10000×10000 个元素时,这对于普通的计算机就变得很困难了。这是因为随着矩阵中元素数量的增加,计算的步骤也会急速增长——矩阵的大小每增加一倍,计算的长度就会增加 8 倍。”
>
> 2009 年提出的算法可以更好地处理更大的矩阵,但必须是稀疏矩阵。在这些情况下,元素之间的关系是有限的,而现实世界中的数据通常不是这样。Zhao 和研究小组提出了一个新的算法,比经典和以前的量子算法版本都快,也没有限制它所计算的数据的种类。
>
> **简单来说,该算法依靠一种被称为量子奇异值估算的技术。** 对于一个 10000 平方的矩阵,经典算法大约花费数万亿量级计算步骤,第一个量子算法需要几万步,而新量子算法只需要几百步。
>
Articles
量子机器学习的历史
-
说起机器学习肯定要提起神经网络,而早在1997年大家就开始陆陆续续讨论quantum neural network(QNN)的模型了,比如Gupta,Bonnell 和 Papini的文章,不过并没有取得很大的进展。2001年后大家好像就比较沉寂了,没有什么新的工作。结果这一沉寂就到了2014年,南非的一个理论物理的组开始认真地考虑这个模型,两个博士生Sinayskiy和Schuld在研究所主任Petruccione的带领下开始考虑Hopfield-type networks的quantum evolution。但是由于非线性是neural核心的一部分,而quantum evolution是unitary的(线性的),这样就有一个本质上的矛盾,所以他们提出应该考虑神经网络的开放量子演化(open quantum evolution/dissipative quantum computing),也就是考虑进环境的非线性的耗散作用[1]。他们的工作引起了比较大的关注,所以今年2017年1月,第一个量子机器学习的summer school就在南非召开(笔者本来也想去打个酱油,结果签证没办下来,哭)。
除了神经网络的量子推广,细胞自动机(automata)和康威(conway)的生命游戏(game of life)也有量子的推广。比如"quantum aspect of life" 这本书,由大名鼎鼎的数学物理学家彭罗斯(Roger Penrose)作序。而最早的细胞自动机的量子推广早在1988年就被量子信息的奠基人之一塞林格(Zeilinger)提了出来[2]。
相比量子的理论模型,量子人工智能的算法发展则更为引人注目。最先应该提的是2009年MIT的Aram Harrow等人提出的HHL量子算法[3],能够以指数快的速度解一个线性方程组。这个算法构成了后来2014年Seth Lloyd他们提出的量子支持向量机的基础(quantum support vector machine,QSVM)[4]。紧随其后又有众多的经典机器学习算法的量子版本被提出来了,比如量子主成分分析(Quantum principal component analysis)[5],量子推荐系统(Quantum Recommendation Systems)[6],贝叶斯网络上的量子推断[7],量子增强学习(quantum reinforcement learning)[8]等等。
除了做机器学习直接的量子推广外,还有一个很重要的方向是用量子物理来解释为什么深度学习这么有效。2014年普林斯顿的两个博士生证明了卷积神经网络可以和变分重整化群可以一一映射起来[9]。MIT宇宙学教授Max Tegmark也从信息提取和重整化的角度来说明为什么深度学习需要"深"[10]。四位计算机科学家也从他们领域的角度分析了量子多体波函数,纠缠,张量网络和卷积神经网络的关系[11]。从机器学习的理论角度上来看,量子信息的理论计算机学家Ronald de Wolf从Probably Approximately Correct(PAC) learning model的量子版本来分析算法的time,query和sample的复杂度[12]。
当然除了物理对机器学习的启发,机器学习对物理的研究也有很大的突破。最广为人知的是去年2016年下半年Troyer他们组发在Science上的一篇文章,用神经网络来解决量子多体问题[13],随后又有研究人员用玻尔兹曼机(Boltzmann machine)来做多体相变,拓扑手性态,量子控制,量子纠错码(quantum error correction),全息(holography)等等。
最后,关于量子信息和机器学习交叉领域更为细致的survey可以参考[14,15](本来想把这两个领域交叉的那张全貌图发上来的,结果知乎上传的图片像素实在是),GitHub上也有一个项目把相关的资料整理得比较全awesome quantum machine learning。我之后也会在我的博客中介绍一下我用Python写的quantum SVM,来识别手写数字6和9(知乎不支持MathJax)。
有什么问题或者建议欢迎评论,或者e-mail给我:[email protected]。
参考文献:
1)Schuld, Maria, Ilya Sinayskiy, and Francesco Petruccione. "The quest for a quantum neural network." Quantum Information Processing 13.11 (2014): 2567-2586.
2)Grössing, Gerhard, and Anton Zeilinger. "Quantum cellular automata." Complex Systems 2.2 (1988): 197-208.
3)Harrow, Aram W., Avinatan Hassidim, and Seth Lloyd. "Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations." Physical review letters 103.15 (2009): 150502.
4)Rebentrost, Patrick, Masoud Mohseni, and Seth Lloyd. "Quantum support vector machine for big data classification." Physical review letters 113.13 (2014): 130503.
5)Lloyd, Seth, Masoud Mohseni, and Patrick Rebentrost. "Quantum principal component analysis." arXiv preprint arXiv:1307.0401 (2013).
6)Kerenidis, Iordanis, and Anupam Prakash. "Quantum recommendation systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.08675 (2016).
7)Low, Guang Hao, Theodore J. Yoder, and Isaac L. Chuang. "Quantum inference on Bayesian networks." Physical Review A 89.6 (2014): 062315.
8)Dong, Daoyi, et al. "Quantum reinforcement learning." IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 38.5 (2008): 1207-1220.
9)Mehta, Pankaj, and David J. Schwab. "An exact mapping between the variational renormalization group and deep learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.3831 (2014).
10)Lin, Henry W., Max Tegmark, and David Rolnick. "Why does deep and cheap learning work so well?." Journal of Statistical Physics (2016): 1-25.
11)Levine, Yoav, et al. "Deep Learning and Quantum Physics: A Fundamental Bridge." arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.01552 (2017).
12)Arunachalam, Srinivasan, and Ronald de Wolf. "A survey of quantum learning theory." arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.06806 (2017).
13)Carleo, Giuseppe, and Matthias Troyer. "Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks." Science 355.6325 (2017): 602-606.
14)Biamonte, Jacob, et al. "Quantum machine learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09347 (2016).
15)Adcock, Jeremy, et al. "Advances in quantum machine learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.02900 (2015).
量子计算的理论发展
-
做量子计算的人常被问的问题就是,『什么是量子计算?』
其实顾名思义,量子计算机就是操控量子信息的计算机。
那么量子信息是什么?它和经典信息有什么不同呢?
量子信息有以下几个特点:
1、量子信息的存储量大。这是根据量子叠加态原理,比如说2个经典比特有4种情况,00,01,10,11,但是这两个比特只能处于其中一个态,就只能存1种的信息;但是量子比特(qubit)可以处于这四种情况的叠加态,就可以存储4种信息。类似的,量子信息存储的量就是经典信息的指数倍。
如下图,|a>=|0101>,而|b>=|0101>+|0101>,后者就是4和5的叠加态,其实后者还可以成为更多的态的叠加态,说明了量子态的存储能力的强大。

2、量子信息可以并行处理。这也是基于叠加态原理,对一个量子信息单元(qubit)做逻辑门操作,其所有的态都在变化,这样就实现了所有的态的统一处理,这是经典计算机所远远达不到的。
如下图,该球(Bloch球)表面的每一点都是|0>和|1>的叠加态(不同点未来在测量的时候坍缩到某一态的概率不同),当我们对量子态进行操作时,它按照量子力学的规律绕某个轴转动,绕不同的轴转动就可以到达球面任意点,这种操作下|0>和|1>是同时变化的,这就是并行处理。

3、量子信息不可克隆。就是量子信息不能被复制,所以不能像经典计算机有copy的逻辑门的功能。
4、量子信息的测量坍缩。量子信息的测量过程中会以不同的概率坍缩到不同的态,而不是一个确定的结果,而且坍缩之后的量子态不能复原,这也是量子信息不可精确克隆的原因,因为一旦精确克隆,就说明你对它做了测量,然而一旦测量就被破坏,所以也就不能精确克隆了。
前两点是量子信息的优点,是广大科研人员的奋斗动力。
然而,后两点就是量子计算的绊脚石,这两个不同寻常的特点直接导致了量子算法设计的困难,也是量子计算机发展这么慢的主要原因。
了解了这些特点,你一定想知道科学家怎么开始设计量子计算机呢?
其实还是要从经典计算机说起。
经典数字电路的模块如下,由与或非等逻辑门构成:

然后数字电路集成之后,就可以实现一些简单的功能,比如数码管显示:

最后,集成电路的发展就催生了CPU,就是我们现代的经典计算机:

那么,根据这一思路,科学们就想,我们的量子计算机也应该由一些逻辑门构成。
然而这其实有些困难,读者可以自己想想哪些经典逻辑门我们可以在量子中实现,哪些不能?
我们下期见!
-
抱歉这么久才更新第二篇,最近会多更新几篇的。
上次说到如何在量子线路中实现类似经典逻辑门的操作,那么,这件事情我们该从何思考起来呢?
对于确定的计算,经典计算机实现的是一个n比特输入,m比特输出的函数
记为
我们可以将上述函数转化为m个函数,每个函数都是一个n比特输入1比特输出的函数
记为
对于
,我们不妨设输出k个1,2^n-k个0,即输入
时输出为1,输入
时输出为0
这样可以写出
的形式
其中,
是或函数,任意一个
的输入为1,则
输出为1
而对于函数
,我们可以写成
其中,
是与函数,当
的各位和等式右边的序列对应相等时(没有上横线的位为1,有上横线的位为0),
为1
到现在为止,我们已经将最初的问题简化为只需要与门、或门、非门外加copy门这些基本逻辑门构成的问题了,简单地想,我们只需要在量子逻辑门中实现这些基本逻辑门就可以实现量子计算了
不过,还需要提到的是,量子计算和经典计算不同的是,它是可逆计算,可以简单地理解为输入和输出的数目相等,在可逆计算理论中,只要实现Toffoli门,就可以实现与或非门等基本逻辑门(这一过程是通过控制三个输入比特中特定的一个或两个输入比特来实现的,读者可以自己思考),那么,我们最后就把问题归纳到如何在量子计算中实现Toffoli门


Toffoli门如图,是一个控制控制非门,只有当最上面两行输入为1时,最下面的输出将输入翻转
在量子力学中,我们知道比特是在Bloch球上的,对于比特的操控我们是通过让比特绕某一轴的旋转来实现的。在这里我们可以轻松实现的是3比特的Deutsch门,即控制控制旋转门,通过级联Deutsch门可以实现Toffoli门
后来的科学家进一步简化了Deutsch门,他们证明通过控制旋转门和控制非门的某种级联可以实现Toffoli门,如图


右面的V代表的是控制旋转门,而控制旋转门又可以表示为单比特旋转门和控制非门


这样,科学家们最后就将通用的量子计算简化为:单量子比特操控和两量子比特控制非门的操控!也就是说,只要我们做出来单比特旋转门和两比特控制非门,理论上我们就可以实现通用的量子计算了!
可是到现在各位可能还看不出来量子计算的威力在哪里,接下里我们介绍一些量子计算的算法,来让大家体会体会量子计算的效果,下期见(不会太久)!
-
今天介绍几种重要的量子算法。
在量子计算的物理实现方面,最重要的莫过于DJ算法,因为它能非常简单地证明量子计算的加速能力。
在应用前景方面,莫过于可以破解RSA公钥体系的Shor算法,和可以解决大部分问题的Grover搜索算法。
所以接下来我们主要关注这三种算法。
一、DJ算法
全称是Deutsch-Jozsa算法,它解决的是这样一个问题:
一个函数
,已知它要么是常数函数要么是平衡函数,通过某种算法来确定f是何种类型的函数。
经典算法做多次访问,若做k次访问,输出结果不完全相同,则必为平衡函数;若做k次访问,输出结果都相同,则可能为常数函数。要想做出准确的判断,这个k必须超过2^(n-1),这个算法的复杂度是随着n的增大而指数增多的
但是采用DJ算法,只需要一步就可以判断是常数函数还是平衡函数,其逻辑门操作如图:


过程如下:
先对输入的n个比特|0>和辅助比特|1>作Hadamard变换,然后经过Uf变换,再对输出比特(不包括辅助比特)进行Hadamard变换即可得到一个可以判断是常数函数还是平衡函数的等式。
第一步Hadamard变换将输入的
转换为


Hadamard变换实际上是将|0>转换为
,将|1>转换为
,多个比特的时候有如下公式:


然后进行Uf变换,这其中Uf起到了决定性作用,它常被称为是quantum oracle,它进行了如下转换
,得到


因为f(x)要么是0要么是1,所以上式可以改写为


再只对输入比特作Hadamard变换,


然后我们以
为基进行测量,落到这个基上的概率是


如果f(x)是常数函数,这个概率就是1;如果是平衡函数,这个概率就是0.
也就是说对于最后的测量,如果落在
上,就是常数函数;如果不落在
上,就是平衡函数,实现了一步解决问题,说明了量子计算相对于经典计算的强大之处。
打字蛮累的,今天就先写到这里,大家能对量子计算的威力有个印象~
-
Grover搜索算法和Shor质因数分解算法是量子计算中最为经典且重要的两个算法。Shor算法利用了量子傅里叶变换和一些数论的理论,非常令人震撼,其在破解银行等领域的密钥方面的作用一直被视为量子计算机的重要应用之一。不过笔者认为Grover算法的意义可能来的更为广泛,首先它的算法复杂度被证明是最优的搜索算法,其次Grover算法可以加速一切NP问题。
算法复杂度理论认为解决问题的范围大概是这样:


P problem指的是可以多项式时间解决的问题,NP problem是可以多项式时间验证的问题,NP包括P,但是为了方便,接下来提到的NP问题特指能够多项式时间验证但不能多项式时间解决的问题;NP complete是NP中最难解决的问题,如果它们被多项式时间内解决,那么所有NP问题都可以被多项式时间解决。BQP是量子计算机可以在多项式时间内解决的问题,一般认为BQP大于P但小于NP,比如质因数分解暂时可以认为是一个NP问题(学术界没有定论),那么Shor算法解决的就是BQP中不在P problem那个范围内的问题了。
Grover算法并没有达到多项式时间的复杂度,经典算法的复杂度是
,它的时间复杂度是
,但是它可以加速一切NP问题(这是因为所有NP问题都可以归并为多项式时间验证的搜索问题),它的应用范围就更加广泛了,像现在云计算和大数据处理,这种根号级别的提速也是非常可观的。
Grover算法逻辑门如图:


前面和DJ算法类似,经过Hadamard变换和Quantum Oracle (Uw),得到


这里的f(x)是Uw引入的函数,当|x>是我们要搜索的对象|w>时,f(x)的值为1;当|x>不是我们要搜索的对象|w>时,f(x)的值为0;我们舍弃辅助比特(|0>-|1>)来观察f(x)的作用,得到
代入f(x),得到


按照如图电路,接下来我们定义
其中
整个过程可以通过一个几何图像了解


|s'>是和待搜索量|w>正交的2^n-1维超平面,经过Hadamard变换得到的|s>经过Uw变换相当于对|s'>做轴对称,然后在经过Us变换,相当于对|s>做轴对称,这样每次完成这个循环,|s>向|w>前进theta角,而theta角满足:
我们将这一步骤重复T次,最终我们希望
,这样就搜索到了想要的|w>,根据计算,当T=
时,搜索到|w>的概率为
,所以量子搜索的次数为
次,而经典搜索是
次,相比之下量子搜索实现了根号级别的加速。
如果要同时有r项满足搜索条件,我们只需要记
,这是只需要搜索
次,但搜索的前提是我们知道r是多少,不然搜索次数不对的话搜索到要找的对象的概率可能是0,一般还会使用量子计数算法先得到求解的数目。
最终电路的实现,主要考虑
,我们知道
表示的意义是当输入比特都为|0>时做相位翻转,这个可以通过n比特相位控制门(n-1个比特都为1时最后一个比特相位翻转,实际上也是整个比特串相位翻转)外加非门实现,而相位控制门可以通过控制非门和Hadamard门实现。对于两比特的搜索,最终完整的电路如图所示:


大家可以自己演算一下两比特的搜索需要几步完成。
下期我们Shor算法见!
如何解读「量子计算应对大数据挑战:中国科大首次实现量子机器学习算法」
(1 封私信 / 83 条消息)如何解读「量子计算应对大数据挑战:中国科大首次实现量子机器学习算法」? - 知乎
1)关于这项工作本身
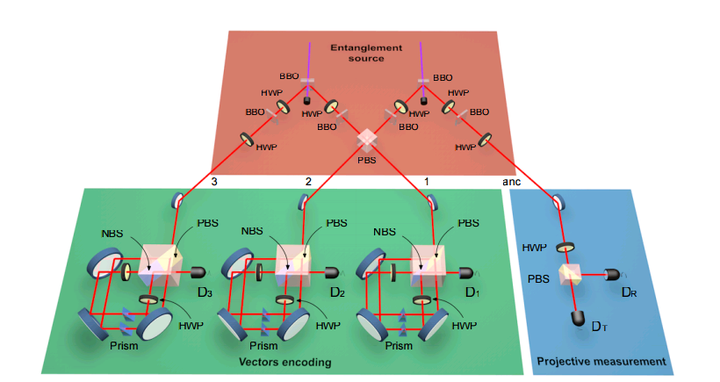
简单来说就是,用光子比特(photonic qubit)作为量子比特,用透镜构成量子逻辑门,整体是一台光量子计算机。
量子光学这套东西,潘教授已经玩得出神入化,几乎甩开其他所有学校了。
取得的成就是用量子计算正确地运行了机器学习算法。
但题目里【首次实现量子机器学习算法】的说法可能不太准确。\ 我猜是因为没有把Dwave算作真正的量子计算机,因为Dwave只能运行量子退火算法。而潘教授研究的这种光量子计算机是通用型的"标准"量子计算机。通用型量子计算机是可以运行所有量子算法的,这就是厉害的地方吧。\ 这项工作的意义就是在于通用型量子计算机第一次成功的运行了量子机器学习算法。\ 之前大家也都知道这个方案肯定可行,但是实验难度很大。
2)未来的障碍\ 通用机这么好,为什么大家不发展通用型量子计算机呢?\ 没有别的原因,就是因为太难了。\ 五十年前大家觉得可控核聚变还有五十年,现在大家觉得可能还要五十年...\ 通用型量子计算机不会比这难度小。
这篇文章里的量子计算机非常初级,只能处理最简单的问题。而且可扩展性很差,按着这种搭光路的方法,可能第一台有实用价值的通用型量子计算机比埃尼阿克还要笨重。
世界上第一台电子计算机ENIAC长30.48米,宽1米,高2.4米,占地面积约170平方米,30个操作台,重达30英吨,耗电量150千瓦,造价48万美元。
甚至这种思路可能没有结果。比特数一高,光路就复杂到再也无法在实验室搭出来。\ 当然集成光学等学科的发展也可能让光量子计算机有所突破。一切都是未知数。
通用型量子计算机还有其他思路,基于核磁共振、基于超导环等等。\ 但暂时还看不出来到底哪条路是对的,所以每一路都养着一大批物理PhD在研究。\ 光量子计算机这条路也只是诸多候选方案之一。有没有光明的未来只有不断尝试才知道。
之前评论区里总有人问我,为什么中国不发展量子计算机?\ 这里就顺便回答一下。量子计算这么重要的东西中国不可能没有发展。但有的东西不是我们想有就能有的。通用型量子计算机什么时候才能有重大突破谁也说不好。现在的每一小步可能都踏在错误的方向上,但是每一小步也都有可能变成真正的一大步。
3)补充一些背景故事
在我本科毕业时,都未曾听说过潘教授的组开始量子机器学习的研究。去年年底的时候,听某位USTC师姐说道,潘组已经开始研究量子机器学习。现在这个应该是初步成果了。\ 本科班上也有同学保研到潘教授组,没记错的话都是专业前几的。大多数本科就参与组内科研的大神。\ 有这么厉害的导师,又有这么优秀的学生,还有多到让人吓一跳的经费,可以发射世界上第一颗量子卫星,现在再达成【首次实现量子机器学习算法】的成就也不让人意外了。
量子机器学习/量子人工智能最近两年在飞速发展。\ 首先是,CIA,没错就是大家熟知的那个美国中央情报局,作为大股东资助的Dwave公司开发出Dwave量子计算机。\ 然后,2013年,美国国家航空航天局NASA和Google联合成立了量子人工智能(Quantum AI Lab)。\ 去年下半年,又发现洛克马丁,嗯,就是那个开发了F16/F117/F22的公司,与牛津大学联合建立了量子优化和机器学习研究中心。
不要问我美帝想干什么,我真的不知道。。\ 作为此领域的一员表示,欢迎各国争先恐后地为人类的未来砸钱。
再来一点题外话。\ 牛津大学真心是一所有独特气质的学校。CS系竟然有一个大组叫Quantum Group。是CS系规模最大的方向之一。专门研究量子物理和计算机交叉的方向,进行各种科幻研究。。不愧是英语世界无数大学的母本。\ 剑桥大学、哈佛大学是牛津一脉相承。\ 东京大学也是以牛津为模板建立的亚洲第一所现代大学。\ 希望牛津可以继续保持这种传承了八百年气质吧。全世界的大学都变成一个样就太无聊了。
再补充一个背景。\ 量子机器学习(Quantum Machine Learning)就是量子计算+机器学习么?\ 不是的。\ 量子机器学习还包括另外一部分,就是用量子力学的思想和模型来改进机器学习算法。\ 【A Quantum-Theoretic Approach to Distributional Semantics】\ 比如说这篇很有名的NLP相关的文章。用密度矩阵表示单词在文本中的信息。词汇相似度用Trace(MN)表示,即两个密度矩阵乘积的迹来表示。为什么要用密度矩阵?因为密度矩阵包含了一个量子系统的所有信息,而我们又可以把一个文本抽象为量子系统。
文本是这样的。
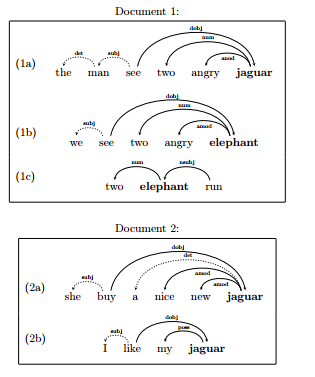 \
量子模型是这样的。
\
量子模型是这样的。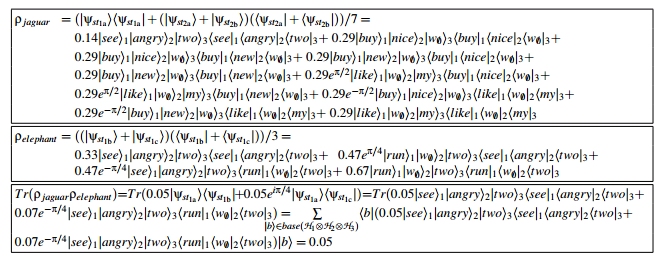
jaguar和elephant两个单词在此文本里的相似度是0.05。\ 这个量子模型的最终效果也胜过现有模型。感兴趣可以自己读读看。
这种思路对机器学习的促进是不受量子计算机发展的限制的,可以直接在电子计算机上运行。
实际上,我导师也一直鼓励我多尝试这个思路。因为除了成果可以直接用,不用等不知道哪天才出现的量子计算机。\ boss第一次发这个领域的顶会是在2009年。他吐槽那个时候那群计算机出身的审稿人根本看不懂量子力学在机器学习里的意义,一篇文章改了快半年才通过。后来情况就好多,大概有3,4篇量子机器学习在ML/AI/NLP的顶会被顺利接受。\ 然后最近几年,CS出身的科学家发表量子机器学习的文章也越来越多,几乎占了半壁江山的感觉。
这大概就是现在的形势了。
这些背景故事告诉了我们,美帝军方水很深,量子机器学习的世界还很广阔。
暂且如此。\ 以上。
Quantum Machine Learning: An Overview
Quantum Machine Learning: An Overview
-
量子计算
量子(Quantum)
量子是任何物理实体(比如能量和质量等)的最小可能单位。1900年,德国物理学家、量子力学创始人马克斯·普朗克(Max Planck)提出,在原子和亚原子水平,一个物体的能量被包含在叫做量子(quanta)的离散数据包中。
波粒二象性(Wave-particle duality)是量子粒子的特征,它是指微观粒子基于不同的环境,有时会表现出波动性,而有时表现出粒子性。
量子理论的特点是找到给定点x在空间中存在的概率,而不是它的确切位置。
△ 光具有例子和波的双重性质
量子位(Qubit)
经典计算机通过经典的“位(bit)”执行操作,这些位不是0就是1,而量子计算机借住的是“量子位(qubits)”。
量子位可被表示为绕核旋转的电子和光子。光子的偏振态和电子的自旋态可用|1>和|0>分别表示。
叠加(Superposition)
量子位同时以0和1的形式存在,这种现象被称为“叠加”。
虽然粒子能存在于多个量子态中,一旦我们确定了粒子的能量或位置,叠加就至此消失,它只能存在一个状态。
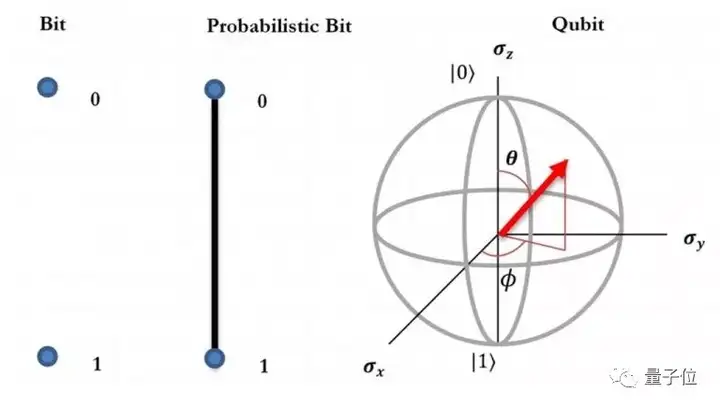
△ 量子位被定义为一对指向单位球面中一个点的复杂向量。一般来说,直指上方(正轴)的量子位表示为列向量|0>,指向下方(负轴)的量子位为行向量|1>。
纠缠(Entanglement)
“量子纠缠”指的是量子粒子之间的相互作用。即使粒子间相隔甚远,它们依然相互作用、相互参照,而不是独立的。
在测量时,如果一对纠缠的量子被决定处于箭头向下的自旋态(能量最低状态),则当电子与它的磁场保持一致时,这个状态就会被传递到另一个相关的箭头向上的相对自旋态的例子上。
量子纠缠允许相隔很远的量子位彼此之间及时相互作用。
讲完这四个基本概念,可能会有个疑问,量子计算是怎样释放出巨大的并行性的?
两个相互作用的经典位有四种状态,即00、01、10或11。每个信息的两个组成成分(第一个位和第二个位)组合起来仅表示给定时间内的二进制结构。向普通计算机添加更多的位仍表示二进制结构。

△ 在测量前的叠加中的量子位具有“自旋向上”和“自旋向下”的概率
一个量子位可同时存在0和1这两种状态。因此,两个相互作用的量子位可被同时存储为4个二进制结构。一般来说,‘n’ 量子位可同时代表 ‘2^n’个经典二进制结构。
因此,一个300量子位的量子计算机能同时探索2^300种可能的结果,因此带来了巨大的并行性。所以,在量子计算机中加入更多的量子位会成倍增加计算能力。
目前,我们的技术还无法实现真正意义上的量子计算机,因为添加更多的量子位和处理亚原子需要低于-452华氏度的低温环境。
因此,微软通过量子模拟器LIQUi|>模拟40量子位的操作,通过微软Azure云计算资源扩展。
量子计算可解决专业的科学问题,如分子建模、高温超导体的产生、药物建模和测试、分子的选择以及有机电池的制造。对于看视频或写Word文档等一般用途的任务,它并不是最佳选择。
-
Quantum SVM
Quantum SVM
-
讲Quantum SVM之前我先介绍一下量子线路(quantum circuit)和Classical SVM的背景知识。
1. 量子线路
量子线路模型十分直观,很符合我们正常物理学家和计算机学家的思维[1]。

EPR pair
上面这个线路就展示了怎么制备一对最大纠缠的量子态(EPR pair)。一般纯态的qubit可以写成这样: |ψ⟩=a|0⟩+b|1⟩|ψ⟩=a|0⟩+b|1⟩,这个量子系统只有两种可能允许的状态|0⟩|0⟩ 和 |1⟩|1⟩, a2a2表示状态|0⟩|0⟩出现的概率, b2b2表示状态|1⟩|1⟩出现的概率。如果取|0⟩=(10)|0⟩=(10)和|1⟩=(01)|1⟩=(01)作为二维线性空间的一个基,那么量子态|ψ⟩|ψ⟩也可以写成一个二维矢量(ab)(ab)。每一条水平线代表一个qubit,最左边是输入的量子态(initial state),比如这里输入|00⟩=|0⟩1⨂|0⟩2|00⟩=|0⟩1⨂|0⟩2,⨂⨂表示1系统和2系统的张量积(tensor product),(ab)⨂(cd)=⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜acadbcbd⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟(ab)⨂(cd)=(acadbcbd)。 中间的符号H,CNOT表示我们对态进行量子门(quantum gate)的操作,经过这两个量子门后,我们就制备了一个Bell态 |ψ⟩=12√(|00⟩+|11⟩)|ψ⟩=12(|00⟩+|11⟩),也就是两个qubits的最大纠缠态。
让我们来复习一下常用的单比特门:
H=12‾√(111-1)X=(0110)Y=(0i-i0)Z=(100-1)S=(100i)T=(100eiπ/4)Rx(θ)≡e-iθX/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2X=(cosθ2-isinθ2-isinθ2cosθ2)Ry(θ)≡e-iθY/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2Y=(cosθ2sinθ2-sinθ2cosθ2)Rz(θ)≡e-iθZ/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2Z=(e-iθ/200eiθ/2)H=12(111-1)X=(0110)Y=(0-ii0)Z=(100-1)S=(100i)T=(100eiπ/4)Rx(θ)≡e-iθX/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2X=(cosθ2-isinθ2-isinθ2cosθ2)Ry(θ)≡e-iθY/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2Y=(cosθ2-sinθ2sinθ2cosθ2)Rz(θ)≡e-iθZ/2=cosθ2I-isinθ2Z=(e-iθ/200eiθ/2)
可以看到Hadamard门把|0⟩|0⟩映射成了12√(|0⟩+|1⟩)12(|0⟩+|1⟩),
H|0⟩=12‾√(111-1)(10)=12‾√(11)=12‾√(|0⟩+|1⟩)H|0⟩=12(111-1)(10)=12(11)=12(|0⟩+|1⟩)
同理我们也可以得到其他单比特门怎么作用在一个量子比特上的。
一个比较重要的双比特门就是上图用的CNOT门,它表示第一个qubit的态控制第二个qubit的态是否发生变化:当第一个是|0⟩|0⟩时,第二个的态保持不变;当第一个是|1⟩|1⟩时,第二个的态由|0⟩|0⟩变成|1⟩|1⟩,由|1⟩|1⟩变成|0⟩|0⟩。当然第一个qubit可以处于叠加态12√(|0⟩+|1⟩)12(|0⟩+|1⟩)。我们可以写出CNOT的矩阵表示
⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜1000010000010010⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟(1000010000010010)
可以看到CNOT把|10⟩|10⟩映射成了|11⟩|11⟩,
CNOT|10⟩=⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜1000010000010010⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜0010⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟=⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜0001⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟=|11⟩CNOT|10⟩=(1000010000010010)(0010)=(0001)=|11⟩
当第一个态是叠加态12√(|0⟩+|1⟩)12(|0⟩+|1⟩),第二个态是|0⟩|0⟩时,它们总的态可以写成12√(|00⟩+|10⟩)=12√(1010)T12(|00⟩+|10⟩)=12(1010)T,同样可以像上面一样通过矩阵乘法得到作用之后的态。
现在我们就能来验证一下上面那个线路图是怎么得到Bell态的了,
CNOT⋅H|00⟩=⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜1000010000010010⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟[⎛⎝⎜⎜12√12√12√-12√⎞⎠⎟⎟⨂(1001)]⎛⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜1000⎞⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟=(12√0012√)T=12‾√(|00⟩+|11⟩)CNOT⋅H|00⟩=(1000010000010010)(121212-12)⨂(1001)=(120012)T=12(|00⟩+|11⟩)
2. 支持向量机
最早的支持向量机早在1963年就被万普尼克等人提出,不过只能用于线性分类,随后1992年他又和其他研究者提出可以用核技巧应用于最大间隔超平面来创建非线性分类器。这个方法一诞生后就由于它良好的分类性能以及清楚的可解释性碾压神经网络,再之后1998年微软研究院的John C. Platt提出序列最小化Sequential Minimal Optimization(SMO)算法更是迅速地提高了SVM的训练效率。SVM是目前最常用,效果最好的分类器之一,并且由于只依赖于支持向量,没有对大数据的要求。由于其能够处理二分类和回归的问题,有很多广泛的应用,比如人脸检测,时间序列预测,系统辨识,金融工程,生物医药信号处理,数据挖掘,生物信息,文本挖掘,基于支持向量机的数据库学习算法,手写体相似字识别等等。
2. 1. 线性分类器的模型
线性svm是定义在特征空间上的间隔最大的二元线性分类器[2]。它的起源可以追溯到logistic回归[3],回想logistic函数(sigmoid函数)hθ(x)=g(θTx)=11+e-θTxhθ(x)=g(θTx)=11+e-θTx 把实数θTxθTx映射到(0,1),其中xx是nn维特征向量,logistic回归的目标就是优化nn维向量θ=(θ1θ2⋯θn)Tθ=(θ1θ2⋯θn)T s.t. 对于标签为y=1y=1的数据xx,hθ(x)≥0.5hθ(x)≥0.5, 而对于标签为y=0y=0的数据xx,hθ(x)<0.5hθ(x)<0.5。我们可以注意到hθ(x)hθ(x)只与θtxθtx有关,θtx>0θTx>0,那么hθ(x)>0.5hθ(x)>0.5,hθ(x)hθ(x)只是个映射,真实的决定权掌握在θTxθTx手里。
把hθ(x)hθ(x)稍微变形一下,用字符ww代替θθ,加上常数偏移b,θTx=wTx+bθTx=wTx+b,那么hθ(x)=g(θTx)=g(wTx+b)=hw,b(x)hθ(x)=g(θTx)=g(wTx+b)=hw,b(x),我们也可以简化一下g(z)g(z),使其简单映射到y=-1y=-1和y=1y=1上
g(z)={1,-1,z≥0z<0g(z)={1,z≥0-1,z<0

在上面这个例子中,两种数据的特征空间是二维的,我们可以用一条直线把它们分开,这条直线就相当于一个超平面,可以用分类函数f(x)=wTx+bf(x)=wTx+b来表示,当f(x)=0f(x)=0时,xx是位于超平面上的一点,而f(x)≥0f(x)≥0对应于y=1y=1的数据点,f(x)<0f(x)<0对应于y=-1y=-1的点。这样当我们把一个新的测试数据点xx输入f(x)f(x),f(x)f(x)就能告诉我们这个测试点是属于哪一类。
我们接下来的任务就是来确定这个超平面f(x)=wTx+bf(x)=wTx+b。最好的超平面应该使得两边的数据点到这条直线的距离之和最大,也就是分隔最大的超平面。

几何间隔
我们需要先表示出几何间隔。如上图,令平面上一个点xixi投影到超平面上的的为x0x0,ww是垂直于超平面的一个向量,γγ为样本xixi到超平面的距离。于是根据平面几何的知识不难得到xi=x0+γw||w||xi=x0+γw||w||,又因为x0x0是超平面上的一点,wTx0+b=0wTx0+b=0,所以几何间隔
γi=|wTxi+b|||w||=y(wTxi+b)||w||=yf(xi)||w||γi=|wTxi+b|||w||=y(wTxi+b)||w||=yf(xi)||w||
对于n个数据点x1,x2⋯,xnx1,x2⋯,xn,几何间隔可以定义为它们的最小值γ=miniγiγ=miniγi。
我们可以令γγ中的分子miniy(wTxi+b)=1miniy(wTxi+b)=1,那么对于所有数据点应该满足y(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,ny(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,n。我们现在的目标就是调整参数ww和bb,使得γ=1||w||γ=1||w||取最大值,并且满足上式约束条件。
说个题外话,SVM和感知机的原理很相似,感知机在1957年就提出来了,是最古老的分类方法之一[4],感知机的模型和SVM的是一模一样的,区别只在于优化感知机的损失函数时是固定的分母|||w|||||w||,求的是所有误分类的样本到超平面的距离之和的最小值γ=minw,b∑xi∈M-y(wTxi+b)γ=minw,b∑xi∈M-y(wTxi+b),MM是所有误分类点的集合。
2. 2. 转化为对偶问题
对于需要满足不等式约束条件的优化问题我们可以加入拉格朗日乘子。原先求max1||w||max1||w||实际上等价于求min12||w||2min12||w||2。考虑拉格朗日函数
ℒ(w,b,α)=12||w||2-∑i=1nαi(yi(wTxi+b)-1)L(w,b,α)=12||w||2-∑i=1nαi(yi(wTxi+b)-1)
如果我们考虑这个函数对于αα的最大值θ(w)=maxαi≥0ℒ(w,b,α)θ(w)=maxαi≥0L(w,b,α),可以发现使得θ(w)θ(w)取最小值的ww正好也能使12||w||212||w||2取最小值,并且满足约束条件y(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,ny(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,n。因为对于不满足约束的ww,比如y(wTxi+b)<1y(wTxi+b)<1,αα可以取∞∞,也就是不管ww怎么取,θ(w)θ(w)对ww的最小值是∞∞,自然没有满足约束的θ(w)θ(w)小。这样原来含约束条件的优化问题就变成了单纯的优化w,bw,b,s.t. θ(w)=minw,bθ(w)=minw,bmaxαi≥0ℒ(w,b,α)≡p∗θ(w)=minw,bθ(w)=minw,bmaxαi≥0L(w,b,α)≡p∗。
调换一下求最大最小的顺序,我们得到原始问题的对偶问题,对用d∗d∗来表示偶问题的最优值,d∗≡maxαi≥0minw,bℒ(w,b,α)d∗≡maxαi≥0minw,bL(w,b,α),而且有d∗≤p∗d∗≤p∗。可以验证,我们这里的函数12||w||212||w||2以及约束条件y(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,ny(wTxi+b)≥1,i=1,⋯,n满足Slater条件和KKK条件,所以能取到等号d∗=p∗d∗=p∗。那么我们就可以直接改成求对偶问题了(之所以改成求对偶问题是因为ℒ(w,b,α)L(w,b,α)对ww和bb的导数比对αiαi的导数好求)。
我们有
∂ℒ∂w=0⇒w=∑i=1nαiyixi∂ℒ∂b=0⇒∑i=1nαiyi=0(1)(1)∂L∂w=0⇒w=∑i=1nαiyixi∂L∂b=0⇒∑i=1nαiyi=0
代入ℒ(w,b,α)L(w,b,α)消去ww和bb(历经千山万水后)得到[2]
ℒ(w,b,α)==-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyjxTixj-b∑i=1nαiyi+∑i=1nαi∑i=1nαi-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyjxTixjL(w,b,α)=-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyjxiTxj-b∑i=1nαiyi+∑i=1nαi=∑i=1nαi-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyjxiTxj
剩下的对αα的优化要用到SMO算法,在这里就不详述了,有兴趣的可以参考[2,5]。
2. 3. 非线性分类的核函数
注意到对一个数据点xx分类时,实际上是把xx代入到f(x)=wTx+bf(x)=wTx+b通过其正负号来进行分类的。根据前面的推导11,分类函数可以重新写成f(x)=∑ni=1αiyi⟨xi,x⟩+bf(x)=∑i=1nαiyi⟨xi,x⟩+b,也就是说要预测一个新的数据点,只要计算它与支持向量的内积xi,xxi,x就好了。
前面介绍的方法只能用于分类线性可分的数据,但实际中的数据大多并不是线性可分的,那么需要把前面的方法推广到线性不可分的数据。我们可以简单地先把之前的特征向量提升到更高维度的向量xi→ϕi(x)xi→ϕi(x),使得数据在高维特征空间线性可分后再套用之前的线性分类函数f(x)=∑li=1αiyi⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩+bf(x)=∑i=1lαiyi⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩+b。

高维映射
但是通常来说高维特征空间是原始空间的指数倍大,在这么大一个空间中计算内积将是非常困难的,如果我们有方法在原始的特征空间计算映射之后的内积⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩,那计算就简便很多了,这种方法就称为核函数方法:K(x,z)=⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩K(x,z)=⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩,这里ϕϕ是从原始特征空间XX到内积特征空间FF的映射。
我们看一下一个简单的核函数的例子。假设我们要分类这样的数据

环状数据
用X1X1和X2X2表示这个二维平面的两个坐标,那么分割曲线是一个二次曲线
a1X1+a2X21+a3X2+a4X22+a5X1X2+a6=0a1X1+a2X12+a3X2+a4X22+a5X1X2+a6=0
可以简单地构造一个五位空间Z1=X1,Z2=X21,Z3=X2Z1=X1,Z2=X12,Z3=X2,Z4=X22Z4=X22,Z5=X1X2Z5=X1X2,在这个新坐标ZZ下,原来的方程可以写成
∑i=15aiZi+a6=0∑i=15aiZi+a6=0
这正好是一个超平面方程!也就是说,如果我们做一个映射ϕ:R2→R5ϕ:R2→R5,将XX按照上面的规则映射为ZZ,那么在新的空间中原来的数据变成线性可分的了。

高维可分
那么我们怎么在原始的空间里计算高维特征空间的内积呢?假设在原始空间里有两个特征向量x1=(η1,η2)Tx1=(η1,η2)T和x2=(ξ1,ξ2)Tx2=(ξ1,ξ2)T,那么映射后的内积为:
⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩=η1ξ1+η21ξ21+η2ξ2+η22ξ22+η1η2ξ1ξ2⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩=η1ξ1+η12ξ12+η2ξ2+η22ξ22+η1η2ξ1ξ2
与此同时,我们还注意到:
(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2=2η1ξ1+η21ξ21+2η2ξ2+η22ξ22+2η1η2ξ1ξ2+1(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2=2η1ξ1+η12ξ12+2η2ξ2+η22ξ22+2η1η2ξ1ξ2+1
如果把原来的映射ϕϕ的基础上缩放一下,加一个常数维度,上面这个式子其实用映射ψψ,
ψ(X1,X2)=(2‾√X1,X21,2‾√X2,X22,2‾√X1X2,1)Tψ(X1,X2)=(2X1,X12,2X2,X22,2X1X2,1)T
之后的内积⟨ψ(xi)⋅ψ(x)⟩⟨ψ(xi)⋅ψ(x)⟩。有后面这个式子的优点就在于我们仍然是在原始的特征空间中进行操作,却达到了在高维空间求内积的效果,达到这种效果的函数就叫做核函数(Kernel Function),这个例子中的核函数就是κ(x1,x2)=(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2κ(x1,x2)=(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2。
使用核函数之后,我们的分类函数就由f(x)=∑ni=1αiyi⟨xi,x⟩+bf(x)=∑i=1nαiyi⟨xi,x⟩+b变成了f(x)=∑ni=1αiyiκ(x1,x2)+bf(x)=∑i=1nαiyiκ(x1,x2)+b,需要优化的对偶问题也由∑ni=1αi-12∑ni,j=1αiαjyiyj⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩∑i=1nαi-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyj⟨ϕ(xi)⋅ϕ(x)⟩变成了∑ni=1αi-12∑ni,j=1αiαjyiyjκ(x1,x2)∑i=1nαi-12∑i,j=1nαiαjyiyjκ(x1,x2)。
这个例子中的核函数κ(x1,x2)=(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2κ(x1,x2)=(⟨x1,x2⟩+1)2是多项式核函数κ(x1,x2)=(ax1⋅x2+r)dκ(x1,x2)=(ax1⋅x2+r)d中的一种,另一种最主流的核函数是高斯核函数(Gaussian Kernel),κ(x1,x2)=exp(-r||x1-x2||2)κ(x1,x2)=exp(-r||x1-x2||2),其中rr大于0。 Sigmoid核函数(Sigmoid Kernel)也是线性不可分SVM常用的核函数之一,表达式为:κ(x1,x2)=tanh(rx1⋅x2+b)κ(x1,x2)=tanh(rx1⋅x2+b)。
3. 量子支持向量机
参考资料:
1.) Nielsen, Michael A., and Isaac Chuang. "Quantum computation and quantum information." (2002): 558-559.
3.) Andrew NG, Lecture notes, Logistic Regression Classification.
4.) 感知机原理小结
5.)Platt, John. "Sequential minimal optimization: A fast algorithm for training support vector machines." (1998).
